N+2 Replication
There are several ways to create fault tolerant systems. One of the most common is simply to duplicate the system. For example in a web application stack, we could have a master database and a slave database, which contain the same duplicated data. Also two web servers and a load balancing system that splits the load among the servers. In case of a hardware failure in a web server or a database the remaining server may be able to handle all the load while the broken one is being repaired. Replication of data and redundancy of servers is one of the reasons that some sites are highly available.
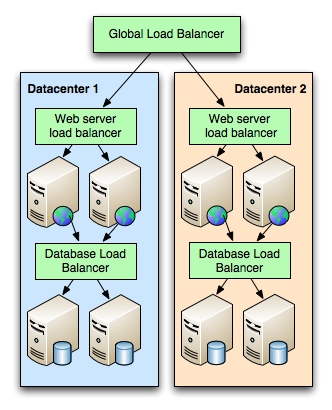
However, duplicating all infrastructure is expensive and inefficient. At the very least it duplicates the costs. If we needed one datacenter with 10 databases and 10 web servers to handle peak load, simply duplicating all the servers would leave us with two identical datacenters, for a total of 20 databases and 20 web servers. One of the datacenters, with 20 machines, would be idle most of the time.
A good compromise between efficiency and cost is N+2 replication. N+2 means that if we need N instances of the system to handle peak load, we should have N+2 instances to ensure availability. Of course, assuming that these instances are independent of each other. Indeed, if the probability that one of the copies fails is p, the probability of having a complete system failure is:
A realistic value for p could be 0.01, which is around 3 days a year. If we take for example N=5, then the availability of the N+2 replicated system is 0.99997%. Which by the same rule of thumb means that it may be unavailable around 15 minutes a year.
The same N+2 reasoning could be applied to other problems outside of computer science and web applications. One trend that is recently becoming popular is that of a perpetual traveler. It is also known as three flag theory. It basically advocates for hedging financial, legal and sovereign risk by splitting personal assets and legal status among different countries or flags.
For example, if Alice is American, lives in the USA and has all her assets in the USA, that renders her vulnerable to a series of risks. Imagine in case of a lawsuit, a US judge can block her bank accounts and seize her assets with the click of a button. Possibly depriving her from the means to defend herself in court. It definitely wouldnt be so easy if she did her banking in Singapore or Hong Kong.